Employee absence analytics can help you identify patterns and trends that undermine your company productivity, calculate direct and indirect costs of different leave types, find areas for improvement in your HR strategy, etc.
In this article, we will unlock the value of employee absence data by showing you how to collect and measure it right and offering tips on increasing presenteeism and employee motivation.
Absence Basics
Absences from work include authorized and unauthorized absence from the workplace, late attendance, or leaving the workplace early.
Depending on the reason, absences can be planned (for example, annual or maternity leave) and unplanned (for example, sickness). Unplanned absences can, in turn, can be divided into excused (caused by force-Majeure circumstances) and unexcused (not justified by any legitimate reasons).
A planned absence is relatively easy to deal with. The manager must ensure the team is appropriately staffed and no projects or critical processes are impacted.
Unplanned absences cause losses, delays, and overwork, as the manager has little or no control over the situation.
Absence analytics can help you act proactively more often than reactively in both cases.
Absence Tracking Methods
There are many ways to track employee attendance, from spreadsheets to complex systems offering vast functionalities. Let’s take a quick look!
Manual methods include all kinds of attendance sheets where employees or managers record their presence, work hours, and/or entry and exit from the office. Though it all sounds like it’s Stone Age, these methods have some undeniable advantages, as they don’t require extra spending, don’t depend on the internet connection, and are extremely easy to implement. The disadvantages include a lack of accuracy, excess paperwork, and long data-processing time.
Partly-automated methods allow users to report their absence via phone call, voicemail, messenger, or social media group. Despite some automation, they have the same disadvantages as the manual methods, as the manager must still transfer all the recorded data into a spreadsheet.
Attendance trackers automate every aspect of attendance management. They reduce human error, streamline data logging, and let employers maintain all the records in one place.
Attendance trackers vary in features, pricing, and target audience. For example, actiPLANS would fit international companies with multiple departments that must ensure the teams are appropriately staffed, and employee absences are always covered.
Your employees can use actiPLANS’ intuitive visual timeline to submit leave requests in a matter of seconds or view their own or their colleagues’ scheduled time off in real time.
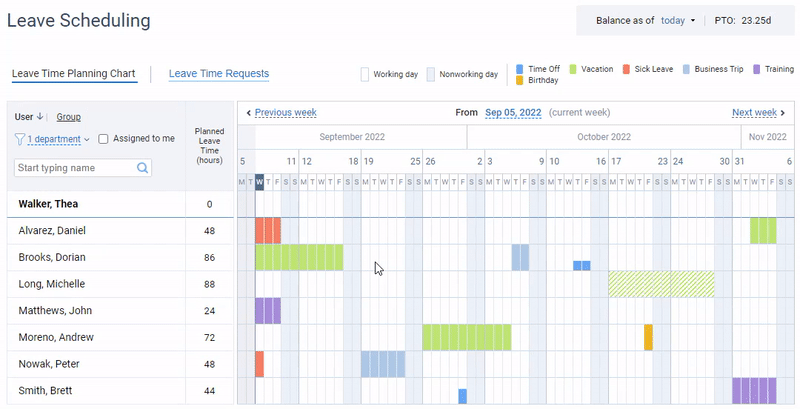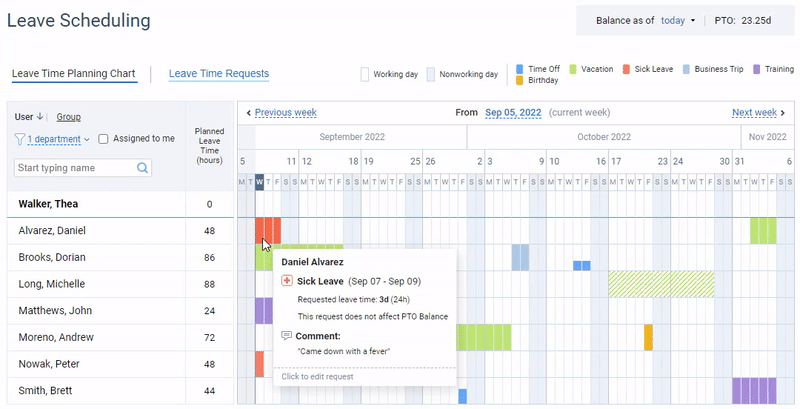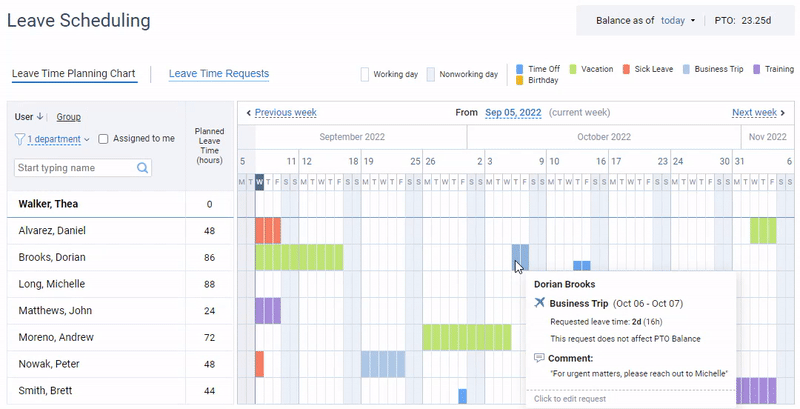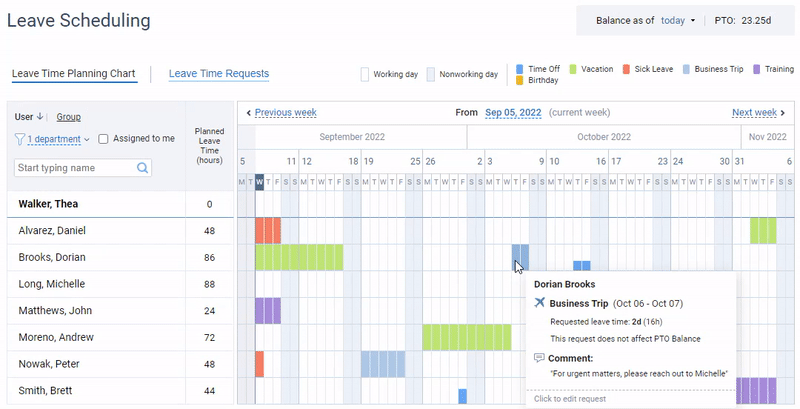
Additionally, actiPLANS lets you create multiple custom leave types, set your own PTO accrual rules, and choose whether to automate the approval of leave requests or run the process manually.
It also offers automated email notifications that promptly inform users of any updates regarding the submitted leave requests.
As for the price, actiPLANS offers a free version for users of up to three members + larger teams can start using actiPLANS at no cost during a 30-day online trial.
Metrics That Matter for Your Business
You can leverage your employee absence data in a variety of ways. For example, suppose you know what part of the year most of your employee vacations fall on. In that case, you can consider seasonal hiring, adjust your project schedule to reduce activity during this period or… whatever.
Below are a few metrics to better understand and manage your workforce, identify potential issues, and improve productivity and profitability.
Personal Absence
Analyzing absence data on individual employees can help you detect absenteeism trends and develop strategies to address the issues behind them.
Example: Let’s say you have two employees that took the same number of sick days across the quarter, but one took 10 days in a row, and another is regularly missing from work on Mondays. Guess where the problem is 😉
Absence by Location or Department
You can analyze absences in a specific team, country, or office. Apart from identifying patterns and trends as described above, you can spot the areas where productivity may be suffering and address the underlying causes or use the data to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Example: Now, let’s consider the members of one team are constantly getting sick. Check their PTO balance. It might happen that they haven’t had a vacation for ages, trying to fulfill a big project in time.
Types of Absence
There are many more absence types than just vacation and sickness: personal days, lieu days, training days, and many more. Collecting data on different absence types can help introduce flexibility and build a positive work environment.
Example: If some of your employees are constantly late to work, as they get into a traffic jam getting to the office from the gym, instead of disciplining them, you can offer to move their shifts.
Absence Costs
Everybody cares about ROI. By tracking absence data in the long term, you can identify areas where labor costs may be higher than expected and take steps to reduce them.
Example: Just calculate how much you spent this year on overtime payments to those who covered for John Doe, and think if you still want to have him on the team.
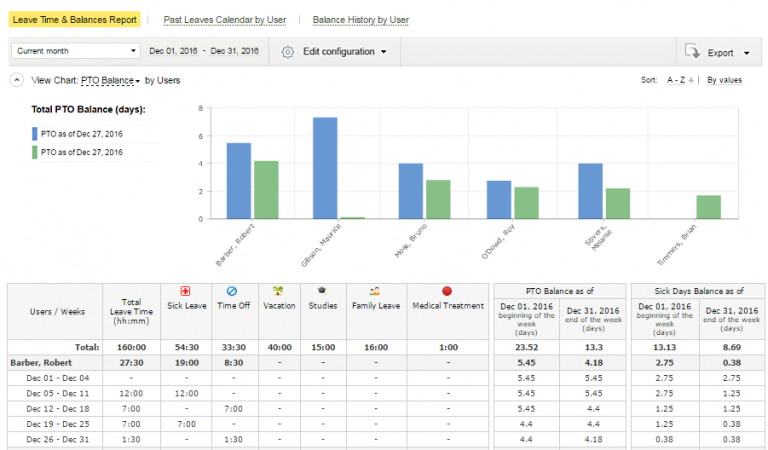
With actiPLANS, you can generate informative and highly customizable reports, enabling your managers to quickly analyze their teams’ leave patterns and make data-driven decisions.
With detailed insights provided by the system, you can optimize workforce planning, increase productivity, and foster a healthier work-life balance for employees.
Absence Rate
The absence rate measures the percentage of total available workdays that employees are absent from work due to illness, injury, or other reasons. It provides insight into absenteeism in the workplace, which can help companies identify potential productivity and cost-saving opportunities.
To calculate the absence rate, follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of workdays available for the period under consideration. This could be a month, a quarter, or a year, depending on the reporting cycle used by the company.
- Determine the total number of days lost due to absence in the same period. This includes all absences, whether due to illness, injury, personal reasons, or vacation days.
- Calculate the absence rate using the following formula:
Absence Rate = (Total Number of Days Lost due to Absence / Total Number of Workdays Available) x 100
Example: If a company has 100 employees and records 200 days of absence in a month with 20 working days, the absence rate would be:
Absence Rate = (200 / (100 x 20)) x 100 = 10%
This means that on average, each employee was absent for 2 days a month, which is equivalent to 10% of the total available workdays.
According to BrightHR, the average absence rate during the COVID pandemic was 1.8%. So healthy absenteeism should not exceed 1.5%.
Lost Time Rate
The lost time rate is the percentage of total available work hours lost due to work-related injuries or illnesses. In the past, it was used by companies to identify areas of the workplace where safety improvements are needed.
In remote teams, it can help to measure the effectiveness of the medical insurance programs in place or serve as an indirect indicator of employee engagement.
To calculate the lost time rate, follow these steps:
- Determine the total hours all employees worked during the period under consideration. This could be a month, a quarter, or a year, depending on the reporting cycle used by the company.
- Determine the total hours lost due to work-related injuries or illnesses during the same period. This includes all hours lost, whether they are due to time off work, reduced productivity, or restricted duties.
- Calculate the lost time rate using the following formula:
Lost Time Rate = (Total Number of Hours Lost due to Work-Related Injuries or Illnesses / Total Number of Hours Worked) x 100
Example: If a company has 100 employees and records 1,000 hours lost due to work-related injuries or illnesses in a month with 20 working days, the lost time rate would be:
Lost Time Rate = (1000 / (100 x 160)) x 100 = 6.25%
This means that, on average, each employee lost 10 hours in the month due to work-related injuries or illnesses, which is equivalent to 6.25% of the total hours worked.
Frequency Rate
The frequency rate (sometimes called severity rate) measures the number of work-related injuries or illnesses per a certain number of hours worked.
The frequency rate allows companies to compare their safety performance to industry benchmarks.
By tracking the frequency rate as well as the lost time rate, companies can measure the effectiveness of their safety programs and implement corrective actions to reduce the risk of work-related injuries or illnesses.
To calculate the frequency rate, follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of work-related injuries or illnesses during the period under consideration. This could be a month, a quarter, or a year, depending on the reporting cycle used by the company.
- Determine the total number of hours all employees work during the same period.
- Calculate the frequency rate using the following formula:
Frequency Rate = (Total Number of Work-Related Injuries or Illnesses / Total Number of Hours Worked) x 200,000
The constant 200,000 is used to standardize the frequency rate to a base of 100 full-time employees working 40 hours per week for 50 weeks per year.
Example: If a company has 100 employees and records 10 work-related injuries or illnesses in a month with 20 working days, and each employee works 8 hours per day, the frequency rate would be:
Frequency Rate = (10 / (100 x 20 x 8)) x 200,000 = 12.5
This means there were 12.5 work-related injuries or illnesses for every 100 full-time employees working 40 hours per week for 50 weeks per year.
Bradford Factor
The Bradford Factor measures employee absenteeism, considering both the frequency and duration of absences. It is calculated by multiplying the number of absences by the number of days absent squared.
The Bradford Factor lets companies identify employees whose absences are having a significant impact on productivity.
The Bradford Factor is also helpful in determining which employees may benefit from additional support or resources, such as wellness programs, flexible working arrangements, or counseling services.
It can also be used to identify potential disciplinary action for employees whose absenteeism is excessive and has a negative impact on the business.
To calculate the Bradford Factor, follow these steps:
- Determine the number of absences an employee has had over a given period (e.g. a year).
- Determine the total number of days the employee was absent due to those absences.
- Square the total number of days absent.
- Multiply the number of absences by the squared total number of days absent.
Example: If an employee has had 3 absences over a year and was absent for a total of 8 days, the Bradford Factor would be:
Bradford Factor = 3 x (8 x 8) = 192
Personio offers the following Bradford Factor Benchmarks:
- Under 50 – an average employee for a typical employee,
- Over 50 – a worrying sign that may require additional monitoring,
- Over 100 – a potential sign of the starting negative trend,
- Over 200 – a situation that may require interference,
- Between 200-500 – a definite issue signal that needs to be addressed,
- Over 500 – potential grounds for dismissal or disciplinary action.
Preventing Unplanned Absences: The Field-Proven Tips from HRs
Preventing unplanned employee absences is important for maintaining productivity and ensuring the smooth operation of the business. Here are some strategies that companies can use to prevent unplanned employee absence:
- Establish effective attendance policies. Ensure that employees are informed about company policies related to illness and absence. Communicate clearly and regularly with employees about expectations, policies, and procedures related to illness and absence. Monitor attendance regularly to identify trends and patterns in unplanned absences.
- Promote flexibility and support. Consider offering flexible work arrangements, such as telecommuting or flexible schedules, to help employees better manage their work-life balance and reduce stress. Offer resources and support for employees dealing with personal or family issues that could lead to unplanned absences. Consider providing access to counseling services or employee assistance programs.
- Address workplace stress. Identify and address sources of workplace stress, such as excessive workloads or poor management practices. Implement strategies to reduce stress, such as time management training or employee assistance programs. Maintain a positive workplace culture that values employees and encourages them to take care of their physical and mental health.
- Improve workplace safety. Ensure the workplace is safe and free from hazards that could cause injury or illness. Provide appropriate training and resources to employees to help them work safely. Encourage employees to take time off when they are sick to prevent the spread of illness in the workplace and promote faster recovery.
- Increase employee engagement. Provide appropriate training and development opportunities to help employees build the skills and knowledge needed to perform their jobs effectively. This can help reduce stress and improve job satisfaction, which can help reduce unplanned absences.



